 Toys Testing Equipment
Toys Testing Equipment Footwear Testing Equipment
Footwear Testing Equipment Tensile Testing Machine
Tensile Testing Machine Environmental Test Chamber
Environmental Test Chamber Building Material Flammability Test Equipment
Building Material Flammability Test Equipment Paper Testing Equipment
Paper Testing Equipment Spectacle Frames Testing Equipment
Spectacle Frames Testing Equipment Oil Analysis Testing Equipment
Oil Analysis Testing Equipment Lab Test Equipment
Lab Test Equipment Electronic Testing Equipment
Electronic Testing Equipment Stationery Testing Equipment
Stationery Testing Equipment Flammability Test Equipment
Flammability Test Equipment Furniture Testing Machine
Furniture Testing Machine Textile Testing Equipment
Textile Testing Equipment
 IP Protection Grade Decryption: Why Does Your Device Need This "Shield"?
IP Protection Grade Decryption: Why Does Your Device Need This "Shield"?- 2026/2/2
- IP Protection Grade Decryption: Why Does Your Device Need This "Shield"? In modern life, electronic devices have become an indispensable part of our daily routines. However, in harsh environmental con...
 How to evaluate the corrosion resistance of lubricating grease?
How to evaluate the corrosion resistance of lubricating grease? - 2026/1/2
- How to evaluate the corrosion resistance of lubricating grease? A comprehensive guide to lubricating grease corrosion resistance testing and professional testing equipment. A tiny corrosion spot in...
 The Hong Kong fire once again rings the alarm: How can laboratories build a safety defense line for building materials through combustion tests?
The Hong Kong fire once again rings the alarm: How can laboratories build a safety defense line for building materials through combustion tests?- 2025/12/25
- The Hong Kong fire once again rings the alarm: How can laboratories build a safety defense line for building materials through combustion tests? The recent serious fire accident in Hong Kong has s...
- More>
SATRA TM55 Detection Method
SATRA TM55 Detection Method
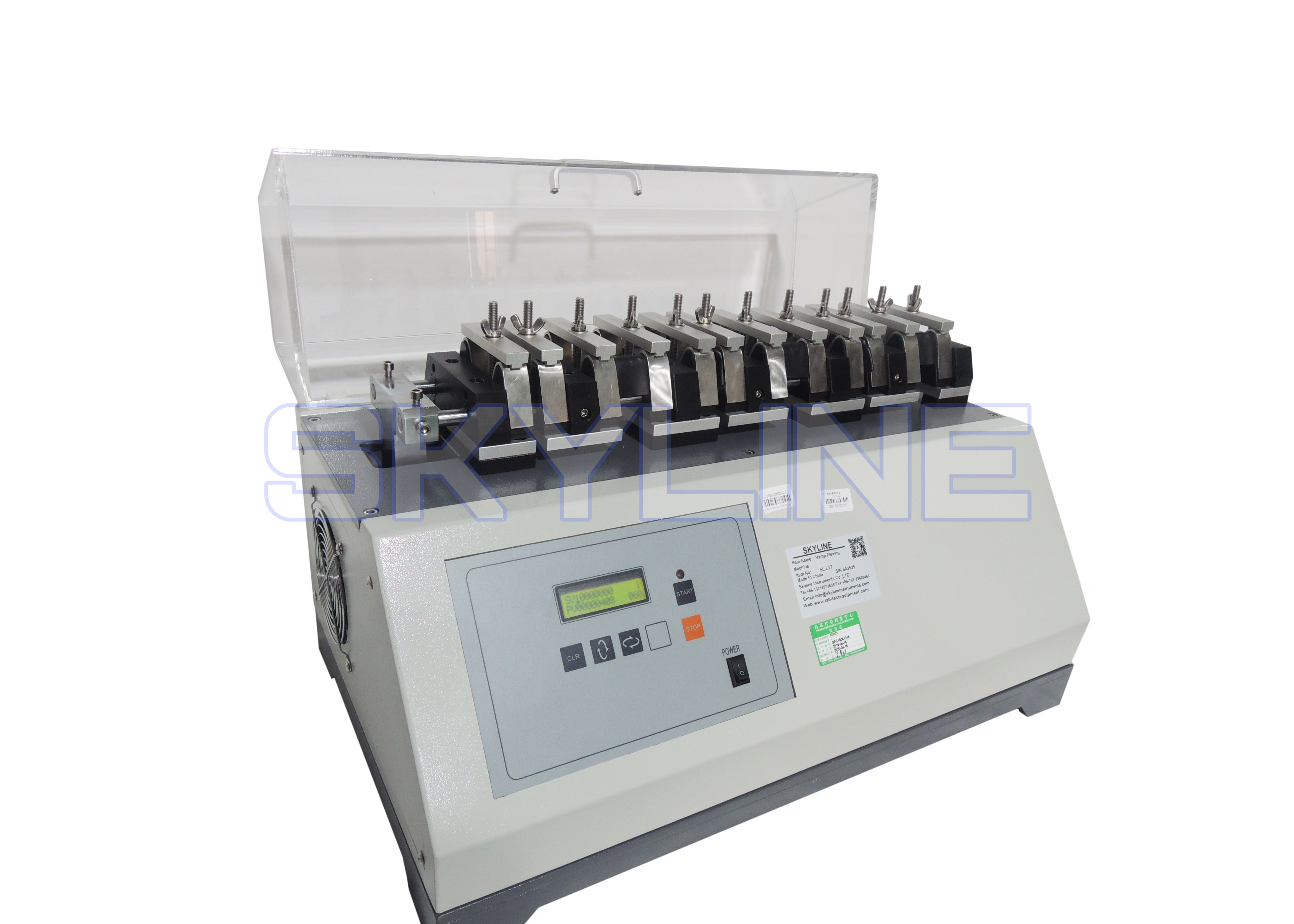
This method is aim to test the flexing resistance of a material tocracking or other types of failure at flexing creases. The method is suitablefor leathers,coated fabrics and textiles used in footwear uppers.
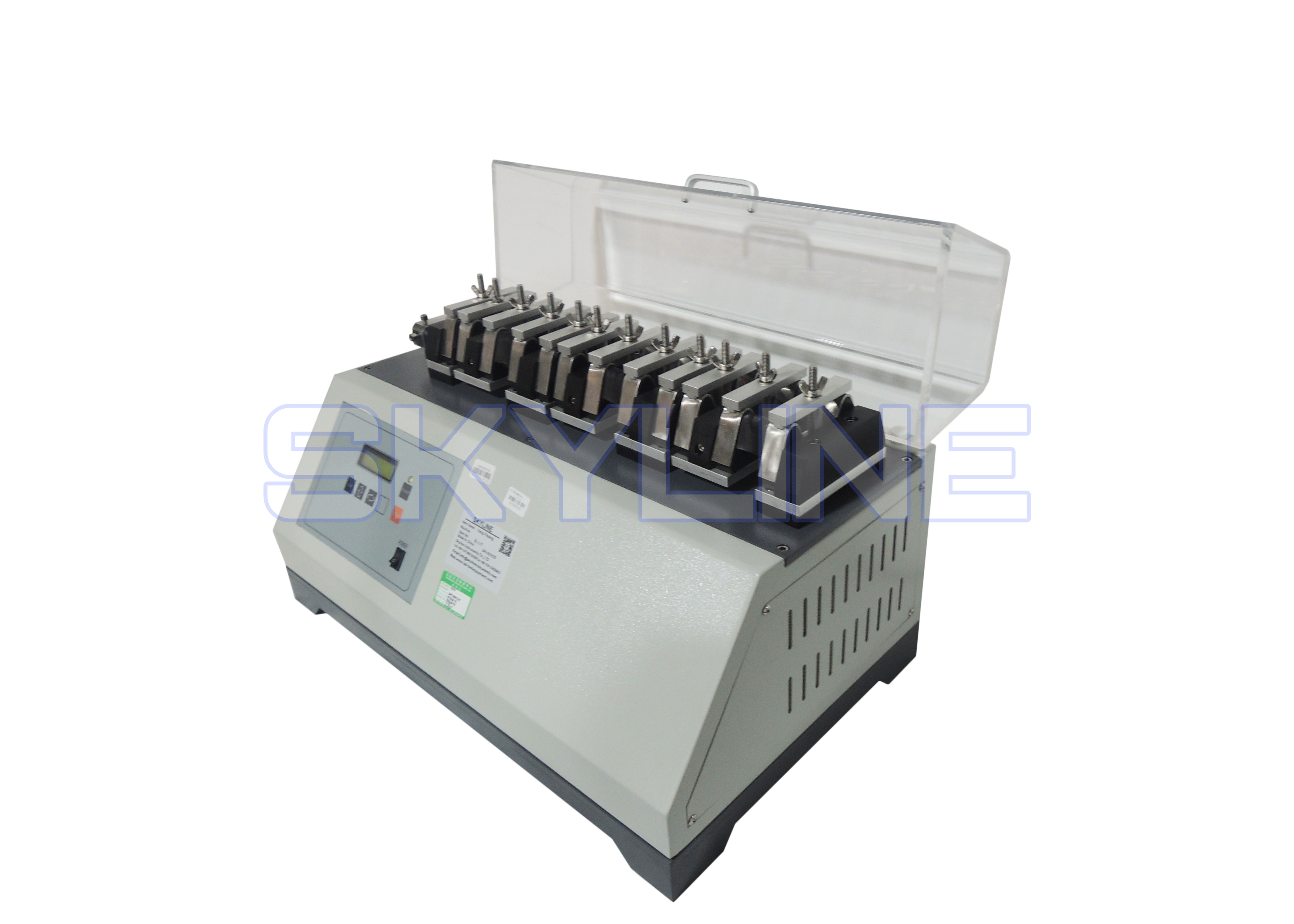

The test material is folded in half then one end is fixed in a clamp. It isthen turned inside out and the free end isfixed in a second clamp at 90 degrees to thefirst. To cause the test material to flex, the first clamp is oscillated through a fixed angle at a defined rate for regular times.At set intervals it is required to record the number of flexing cycles and visually assess thedamage to the test material.The test can be conducted with wet ordry test materials and at ambient or sub-zero temperatures.
Procedure:
1. Place any test materials that are to be tested wet onto the surface with their reverse face uppermost. Spot 1 cm3 of distilled water on to the reverse surface of the test material and use the glass rod to work it uniformly into the material, to within 5 mm of the edge. It usually takes between 1 and 2 minutes for the material to absorb the water.
2. Put the upper clamp of the flexing machine in a horizontal level.
3. For footwear lining materials, fold a test material along the longer centre line with the wearing surface or grain outwards.
4. Insert one end of the folded test material into the upper clamp, and fix the test material in position.
5. Fold the test material inside out round the upper clamp,while the wearing surface or grain is now facing outwards.
6. Apply just sufficient hand tension to the test material to make it taut and there is no obvious bagginess around the top clamp. Fix it in the lower clamp. Finally repeat the procedure from sections 6.2 to 6.6 for the remaining test material(s) or until all of the pairs of clamps are full.
8. Select a series of inspection stages. Suitable inspection stages are including as follows:Dry testing - 10 000,25 000, 50 000 and 100 000 flexing cycles.Wet testing - 1000,2000,5000 and 10 000 flexing cycles.Cold testing - 1000,2000,5000 and 10 000 flexing cycles.
9.Operate the flexing machine at a rate of 100 ± 5 flexing cycles per minute.
10. stop the machine when the first inspection stage reaches.
For each test material, use the magnifying device to assess the flexing damage.Record the damage as the following descriptions:
n No effect or slight creasing or piping.
n Marked or severe creasing or piping.
n Slight cracking.
n Marked cracking.
n Severe cracking.
n Complete failure.
11. Restart the machine and repeat the procedure in sections 6.9 and 6.10 at successive inspection stages until either complete failure occurs or the end of the test is reached.
12. Record the type and severity of damage at each inspection stage with the corresponding number of flexing cycles.
Test Report:
1. Reference to this test method SATRA TM55: 1999.
2. A description of the test material.
3. The condition of test materials tested:wet or dry.
4. The temperature of testing.
5. The type and severity of damage to each test material at each inspection stage.
SATRA can help members interpret the results of this test method.
If you have any demand for SATRA TM55 testing equipment, please let me know.
More details please refer to http://www.lab-testequipment.com/Vamp-Flexing-Machine.html

- ·IS 9873-4 /ISO 8124-4 Horizontal Thrust Tester for Swings and Slide
- ·ISO 8124-4 Dynamic Testing Machine For Barriers / Handrails
- ·ASTM D3512 Random Tumble Pilling Tester
- ·BS476-6 Building Materials Fire Propagation Index Tester
- ·IEC 60331-11 Wire And Cable Fire Resistance Tester
- ·AS1334.10-1994 Propane Gas Building Materials Flammability Tester AC 220V 52Hz 100W

 Toys Testing Equipment
Toys Testing Equipment Footwear Testing Equipment
Footwear Testing Equipment Tensile Testing Machine
Tensile Testing Machine Environmental Test Chamber
Environmental Test Chamber Building Material Flammability Test Equipment
Building Material Flammability Test Equipment Paper Testing Equipment
Paper Testing Equipment Spectacle Frames Testing Equipment
Spectacle Frames Testing Equipment Oil Analysis Testing Equipment
Oil Analysis Testing Equipment Lab Test Equipment
Lab Test Equipment Electronic Testing Equipment
Electronic Testing Equipment Stationery Testing Equipment
Stationery Testing Equipment Flammability Test Equipment
Flammability Test Equipment Furniture Testing Machine
Furniture Testing Machine Textile Testing Equipment
Textile Testing Equipment

 English
English 中文
中文 Español
Español française
française العربية
العربية Русский
Русский







